Understanding Gear Ratios for Bullnose Trucks: Choosing the Right Setup for Your Needs
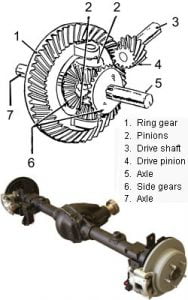
If you’re working with a classic Bullnose Ford truck (1980-1986), choosing the right gear ratio is critical to ensuring your truck performs as you want it to. Whether you’re looking to maximize fuel efficiency, towing capacity, or off-road capability, understanding how gear ratios work and which were available in these trucks is key.
In this article, I’ll walk you through everything you need to know about gear ratios for Bullnose trucks, including what gear ratios were available with different axles, how to read them off the differential tag, and how to choose the right one for your specific needs.
What Are Gear Ratios and How Do They Work?
At a basic level, a gear ratio is a numerical expression of the relationship between the number of rotations of the drive shaft and the number of rotations of the wheels. In a Bullnose truck, this relationship determines how much torque is delivered to the wheels and how fast the truck will move relative to engine RPM.
For example, if you have a 3.50:1 gear ratio, the drive shaft will spin 3.5 times for every full rotation of the wheels. Lower numbers (like 3.00:1) are considered “taller” gears, meaning less torque but more speed at lower RPMs. Higher numbers (like 4.10:1) are considered “shorter” gears, meaning more torque but higher RPMs at a given speed.
The gear ratio you choose will affect several things:
- Acceleration: Lower ratios (higher numbers) provide more torque, which means better off-the-line acceleration. This is useful for towing or off-roading.
- Fuel Efficiency: Higher ratios (lower numbers) reduce engine RPMs at cruising speeds, potentially improving fuel economy.
- Top Speed: Lower ratios can give you a higher top speed at the cost of slower acceleration.
- Towing Capacity: Higher ratios give you more pulling power, which is crucial for towing.
Gear Ratios Available for Bullnose Trucks
Ford offered a variety of axles and gear ratios for Bullnose trucks depending on the engine, transmission, and intended use. The most common axle types you’ll find are:
Ford 8.8-Inch Rear Axle
This axle first appeared in 1983 and became a popular choice for F150s due to its balance between strength and weight. The available gear ratios include:
- 2.73:1: Optimized for fuel economy and highway driving.
- 3.08:1, 3.27:1, 3.31:1: Balanced for general use with decent performance and fuel economy.
- 3.45:1, 3.55:1, 3.73:1: General-purpose ratios, with 3.73:1 providing a strong balance between acceleration and towing.
- 4.10:1, 4.56:1, 5.14:1: Best for heavy towing, off-road use, or performance builds.
Ford 9-Inch Rear Axle
The Ford 9-inch is famous for its durability, and it came with a range of gear ratios that fit various applications:
- 3.00:1: Great for fuel efficiency and lower RPMs on the highway.
- 3.50:1, 3.55:1: Ideal for mixed-use, offering both performance and economy.
- 4.10:1, 4.11:1: Best suited for towing or performance, where torque and low-end power are needed.
Dana 44 Front Axle
This axle was paired with the rear differentials in 4×4 Bullnose trucks and provided good all-around performance for off-road and utility use:
- 3.54:1, 3.73:1: Balanced ratios for 4x4s with light to moderate off-road use.
- 4.09:1, 4.10:1: Ideal for more torque-intensive off-road situations.
Dana 60 Rear Axle
Common in heavy-duty models like the F250 and F350, this axle was built for high load and towing capacities:
- 3.54:1, 3.73:1: For general-purpose heavy hauling or off-roading.
- 4.10:1, 4.56:1: For extreme towing or serious off-road performance.
How to Read Gear Ratios Off the Differential Tag

To determine your truck’s gear ratio, the easiest method is to check the differential tag located on the rear axle. In my case, the tag on my donor vehicle says “S838B,” which I found out refers to a 3.55:1 non-limited slip differential. The first two characters often indicate the axle type, and the letters or numbers after them hint at the specific ratio or type of differential.
If you’re looking for a comprehensive list of tag codes, ratios, and their corresponding differentials, check out this detailed resource:
👉 Fordification’s Differential Tag Codes List.
This will help you cross-reference your differential tag with the axle type and gear ratio.
Choosing the Right Gear Ratio for Your Bullnose Truck
Daily Driving & Highway Use
For those who primarily use their Bullnose trucks for highway driving or commuting, a taller gear (lower numerical ratio) will offer better fuel economy and keep engine RPMs low at cruising speeds. Ideal ratios are:
- 3.00:1 to 3.55:1: A 3.08:1 gear ratio provides a great balance between cruising speed and economy.
Off-Roading
For serious off-road use, where torque and low-speed control are essential, a shorter gear (higher numerical ratio) gives you more torque to tackle steep inclines and rough terrain:
- 3.73:1 to 4.10:1: A 4.10:1 ratio provides maximum torque for off-road capability.
Towing and Hauling
If towing is a priority, you’ll need a shorter gear to provide the necessary low-end torque for pulling heavy loads. Ideal ratios include:
- 3.73:1 to 4.56:1: A 4.10:1 gear ratio is well-suited for most towing needs.
Performance & Speed
For those interested in speed or performance driving, a taller gear provides higher top speed at the cost of acceleration:
- 3.00:1 to 3.55:1: A 3.55:1 ratio balances performance with moderate acceleration.
Conclusion
Choosing the right gear ratio for your Bullnose truck is all about balancing performance, economy, and functionality based on your intended use. Whether you’re looking for fuel efficiency, towing power, or off-road prowess, Ford offered a variety of axle options and ratios to meet your needs. By understanding how these ratios work and cross-referencing your truck’s differential tag, you can optimize your Bullnose for whatever road lies ahead.

If you want more specific information on Bullnose Ford Trucks, check out my YouTube Channel!
For more information on Bullnose Fords, you can check out the BullnoseFord SubReddit or Gary’s Garagemahal. Both are excellent resources.